티스토리 뷰
책 : 밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝 1 chapter 5.7
신경망 학습의 큰 그림
1. 미니배치 : 훈련 데이터 중 무작위로 뽑는다. 선별된 데이터를 미니배치라 한다. 미니배치의 손실함수 값을 줄이는 것이 목표
2. 기울기 산출 : 미니배치의 손실함수 값을 줄이기 위해 각 가중치의 매개변수의 기울기를 구한다. 기울기는 손실함수의 값을 최소화하는 방향으로 제시한다.
3. 매개변수 갱신
가중치 매개변수를 기울기 방향으로 조금씩 갱신한다.
4. 반복
1~3을 반복한다.
1. 2층 신경망 구현
오차역전파법을 이용해 2층 신경망 구현을 위한 class는 다음과 같다.
(층이 늘어난다면, 계층 생성 과정을 늘려주기만 하면 된다.)
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 부모 디렉터리의 파일을 가져올 수 있도록 설정
import numpy as np
from common.layers import *
from common.gradient import numerical_gradient
from collections import OrderedDict
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, weight_init_std = 0.01):
# 가중치 초기화
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
# 계층 생성
self.layers = OrderedDict()
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = Relu()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.lastLayer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
# x : 입력 데이터, t : 정답 레이블
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return self.lastLayer.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
# x : 입력 데이터, t : 정답 레이블
def numerical_gradient(self, x, t):
loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
grads['W1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W1'])
grads['b1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b1'])
grads['W2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W2'])
grads['b2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b2'])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.lastLayer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 결과 저장
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads여기서 numerical_gradient는 기존의 수치미분을 이용한 미분 결과이고, gradient는 역전파를 이용한 미분 결과이다. 두 개를 같이 구현한 것은 오차역전파법 자체가 구현이 까다롭고, 일반적인 수치 미분을 이용한 것은 구현이 쉽지만 성능면에서 오차역전파법이 더 좋기 때문에 올바른 구현을 했는지 확인하기 위해서이다.
2. 기울기 검증
오차역전파법으로 구한 기울기가 올바른지 수치미분과 비교하여 검증한다. 컴퓨터로 연산 시 실제 두 결과가 정확히 일치하기는 힘들지만, 두 결과의 차이가 0에 가까운 수치라면 올바른 기울기를 얻었다고 할 수 있다.
검증 코드는 다음과 같다.
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
from two_layer_net import TwoLayerNet
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True)
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10)
x_batch = x_train[:3]
t_batch = t_train[:3]
grad_numerical = network.numerical_gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
grad_backprop = network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
for key in grad_numerical.keys():
diff = np.average(np.abs(grad_backprop[key] - grad_numerical[key]))
print(key+":"+str(diff))결과
W1:4.616025829193169e-10
b1:3.0318751718016927e-09
W2:5.67817850081448e-09
b2:1.4063203458841711e-07매개변수인 W, B의 기울기 차이가 거의 없음을 알 수 있고, 오차역전파법으로 기울기를 잘 구했다는 것이다.
3. 신경망 학습 구현
기울기를 오차역전파법으로 계산하여 신경망 학습을 진행하자.
훈련데이터를 이용해 학습 후, 테스트 데이터를 통해 제대로 된 학습이 이루어졌는지 확인한다. 여기서 확인은 데이터 양이 많으므로 epoch을 이용한다.
구현 코드
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir)
import numpy as np
from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
from two_layer_net import TwoLayerNet
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True)
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size=784, hidden_size=50, output_size=10)
iters_num = 10000
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
train_loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
for i in range(iters_num):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
grad = network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
for key in ('W1', 'b1', 'W2', 'b2'):
network.params[key] -= learning_rate * grad[key]
loss = network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
if i % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = network.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
test_acc = network.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
plt.plot(train_acc_list, label="train_accuracy")
plt.plot(test_acc_list, label="test_accuracy")
plt.xlabel('epoch (600round=1epoch)')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()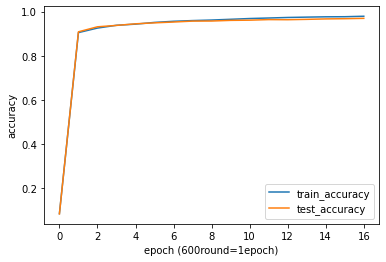
거의 일치하므로 훈련데이터를 통해 잘 학습되었음을 알 수 있다.
'딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 매개변수 갱신 방법 성능 비교 (0) | 2021.01.15 |
|---|---|
| 매개변수 갱신 (0) | 2021.01.15 |
| 오차역전파법 - Affine, Softmax 구현 (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| 오차역전파법 - 활성화 함수 계층 구현하기 (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| 오차역전파법 - 계산 그래프 (0) | 2021.01.13 |
