티스토리 뷰
위상정렬은 DAG (방향성 있고, 비순환 그래프) 에서 방향성에 따라 탐색을 진행시키는 정렬 방식입니다.
예를 들어 그래프가 아래와 같을 때
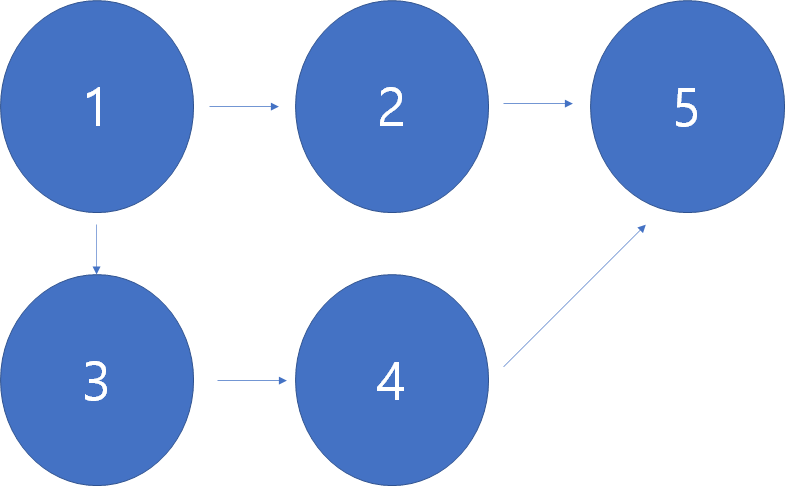
1부터 시작한다면 1 다음 탐색될 노드는 2,3
2 다음 탐색될 노드는 5이지만 아직 4가 끝나지 않았으므로 보류
3 다음 탐색될 노드는 4
4 다음 탐색될 노드는 5
=> 1 2 3 4 5 순으로 탐색이 진행되는 정렬 방식입니다.
위상정렬은 DAG에서 일의 순서를 정해야 하는 문제 등에서 주로 사용됩니다.
방향성을 일의 처리 순서로 보는 것입니다.
위상정렬은 다음과 같이 이루어집니다.
1. 각 노드의 in degree 를 구한다.
2. in degree 가 0 인 노드를 큐에 넣는다.
3. 큐에 있는 노드를 대상으로 탐색을 하면서, 해당 노드와 연결된 노드의 in degree를 엣지 수만큼 감소시킨다.
4. 2,3을 반복한다.
단순히 한 가지 케이스에 대해서 탐색시키는 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
(위 예시에서도 2,3 순으로 탐색하던 3,2 순으로 탐색하던 상관은 없음)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void get_inDegree(int inDegree[], vector<int> graph[], int nodeNum)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
for(auto nextNode : graph[i]) {
inDegree[nextNode]++;
}
}
}
void topological_sort(int inDegree[], vector<int> graph[], int result[], int nodeNum)
{
// 위상 정렬 :
// DAG 그래프에서
// indegree 0 인 것 기준으로 탐색 진행
// 탐색 중인 노드(indegree == 0)와 연결된 노드의 indegree를 연결된 엣지 수만큼 감소시킴
// 해당 노드의 indegree 0 이 되면 해당 노드도 큐에 넣음을 반복
// 이를 이용해서 방향성에 따른 순서 정할 수 있음
queue<int> q;
// 초기에 indegree == 0 인 노드
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
if(inDegree[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
}
// 위상 정렬 진행
int idx = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
result[idx] = node;
idx++;
for(auto nextNode : graph[node]) {
inDegree[nextNode]--;
if(inDegree[nextNode] == 0)
q.push(nextNode);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int nodeNum = 5;
int *inDegree = new int[nodeNum+1];
vector<int> *graph = new vector<int>[nodeNum+1];
int *result = new int[nodeNum+1];
// 1 -> 2, 1 -> 3
// 2 -> 5
// 3 -> 4
// 4 -> 5
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
inDegree[i] = 0;
result[i] = 0;
}
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[1].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(5);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(5);
get_inDegree(inDegree, graph, nodeNum);
topological_sort(inDegree, graph, result, nodeNum);
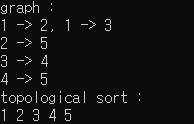
cout << "graph : \n";
cout << "1 -> 2, 1 -> 3\n";
cout << "2 -> 5\n";
cout << "3 -> 4\n";
cout << "4 -> 5\n";
cout << "topological sort : \n";
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
delete[] inDegree;
delete[] graph;
delete[] result;
}
그렇다면 위 예시에서 1 다음으로 2를 탐색하던 3을 탐색하던 상관이 없다면, 전체 탐색 케이스를 구하려면 어떻게 해야 할까도 재밌는 생각거리입니다.
방법은 bfs 방식의 위상정렬 대신 dfs + 백트래킹 방식으로 위상정렬을 모든 노드에 대해 시행하면 됩니다.
위상정렬의 방식을 그대로 가져가면서 현재 노드의 탐색이 끝나면 백트래킹으로 직전 탐색 시 수행했던 방문 여부와 indegree 감소를 다시 원래대로 돌려주면 됩니다.
코드는 다음과 같습니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void get_inDegree(int inDegree[], vector<int> graph[], int nodeNum)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
for(auto nextNode : graph[i]) {
inDegree[nextNode]++;
}
}
}
void all_topological_sort(int inDegree[], vector<int> graph[], bool visited[], vector<int> &result, vector<vector<int>> &allResult, int nodeNum)
{
bool flag = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
// 아직 방문 안 했고, in degree == 0 인 경우
if(inDegree[i] == 0 && visited[i] == false) {
for(auto nextNode : graph[i]) {
inDegree[nextNode]--;
}
result.push_back(i);
visited[i] = true;
// 현재 탐색 노드 기준으로 다시 dfs 탐색
all_topological_sort(inDegree, graph, visited, result, allResult, nodeNum);
// 백트래킹을 위해 원래 상태로 복구
visited[i] = false;
result.pop_back();
for(auto nextNode : graph[i]) {
inDegree[nextNode]++;
}
flag = true;
}
}
// 모든 노드 방문 시, topological sort 완료
if(flag == false) {
allResult.push_back(result);
}
}
int main()
{
int nodeNum = 5;
int *inDegree = new int[nodeNum+1];
vector<int> *graph = new vector<int>[nodeNum+1];
bool *visited = new bool[nodeNum + 1];
vector<int> result;
vector<vector<int>> allResult;
// 1 -> 2, 1 -> 3
// 2 -> 5
// 3 -> 4
// 4 -> 5
for(int i = 1; i <= nodeNum; i++) {
inDegree[i] = 0;
visited[i] = false;
}
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[1].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(5);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(5);
get_inDegree(inDegree, graph, nodeNum);
all_topological_sort(inDegree, graph, visited, result, allResult, nodeNum);
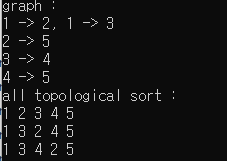
cout << "graph : \n";
cout << "1 -> 2, 1 -> 3\n";
cout << "2 -> 5\n";
cout << "3 -> 4\n";
cout << "4 -> 5\n";
cout << "all topological sort : \n";
for(auto res : allResult) {
for(auto node : res) {
cout << node << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
delete[] inDegree;
delete[] graph;
delete[] visited;
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 벨만 포드 정리 C++ (2) | 2024.04.21 |
|---|---|
| 플로이드 워셜 C++ (0) | 2024.04.21 |
| 다익스트라 C++ (heap으로 빠르게 계산 포함) (0) | 2024.04.21 |
| binary search 구현 C++ (중복 가능, 값 없는 경우 포함) (1) | 2024.04.20 |
| permutation, combination 구현 C++ (0) | 2024.03.09 |
