티스토리 뷰
C++ algorithm 라이브러리에는 lower_bound와 upper_bound가 있다.
이는 오름차순으로 정렬되어 있는 vector 등에서 특정 값을 binary search를 이용해 해당 값이 위치하는 iterator를 리턴한다.
lower_bound(iter1, iter2, data) : iter1 ~ iter2 사이에서 data 이상인 값 중 가장 작은 값의 iterator
upper_bound(iter1, iter2, data) : iter1 ~ iter2 사이에서 data 초과인 값 중 가장 작은 값의 iterator
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void lowerBoundVec(vector<int> &vec, int num)
{
auto it = lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), num);
int idx = it - vec.begin();
cout << num << "'s lower bound index : " << idx << '\n';
}
void upperBoundVec(vector<int> &vec, int num)
{
auto it = upper_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), num);
int idx = it - vec.begin();
cout << num << "'s upper bound index : " << idx << '\n';
}
int main()
{
vector<int> vec = {1,1,3,3,3,5,5,6};
lowerBoundVec(vec, 3);
lowerBoundVec(vec, -1);
lowerBoundVec(vec, 8);
upperBoundVec(vec, 3);
upperBoundVec(vec, -1);
upperBoundVec(vec, 8);
}

C++의 set, map은 red black tree로 이루어져 있으므로 대소비교가 가능하다. 따라서 이에도 lower_bound, upper_bound가 있다.
사용법은 동일하게 lower_bound : 찾고자 하는 값 이상인 것 중 가장 작은 값
upper_bound : 찾고자 하는 값 초과인 것 중 가장 작은 값
이다.
하지만 vector와의 차이점은 index가 없다. 따라서 end 인 케이스를 잘 구분해주어야 한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(9);
cout << "lower bound : \n";
auto it = s.lower_bound(0);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.lower_bound(1);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.lower_bound(2);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.lower_bound(3);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.lower_bound(10);
if(it == s.end())
cout << "end!!!\n";
cout << "upper bound : \n";
it = s.upper_bound(0);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.upper_bound(1);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.upper_bound(2);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.upper_bound(3);
cout << *it << '\n';
it = s.upper_bound(10);
if(it == s.end())
cout << "end!!!\n";
}

이를 조금 더 응용하면 다음 분야에 사용할 수 있다.
[a, b) 꼴로 이루어진 범위가 있다. 이 때 set을 이용해 새롭게 입력되는 [x, y) 가 겹치는 영역이 있는 지 유무를 판단할 수 있다.
따라서 다음을 작성하겠다.
1. set 내에 겹치는 범위는 없어야 한다.
2. 입력 [x, y) 가 set 내의 값과 겹치는 것이 있으면 false를 리턴, 없다면 true 리턴 및 insert
prev, next 는 iterator 라이브러리에 있는 것으로 직전, 직후 iterator를 리턴한다. set이 iterator 라이브러리를 포함하므로 별도로 include 하지는 않았다.
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
bool overlap(const pair<int, int> &p1, const pair<int, int> &p2)
{
// p1, p2 겹치는 지 유무 (p1, p2 : [x,y) 꼴 가정)
if(p1.first < p2.first)
return p1.second > p2.first;
else if(p1.first == p2.first)
return true;
else
return p2.second > p1.first;
}
bool insertion(set<pair<int, int>> &s, pair<int, int> p)
{
auto it = s.lower_bound(p);
if(it == s.begin()) {
if(overlap(*it, p))
return false;
}
else if(it == s.end()) {
// 마지막 거와 체크
auto prevIt = prev(it);
if(overlap(*prevIt, p))
return false;
}
else {
auto prevIt = prev(it);
if(overlap(*prevIt, p) || overlap(*it, p))
return false;
}
s.insert(p);
return true;
}
void printSet(set<pair<int, int>> &s)
{
cout << "set : \n";
for(auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) {
cout << (*it).first << ", " << (*it).second << '\n';
}
}
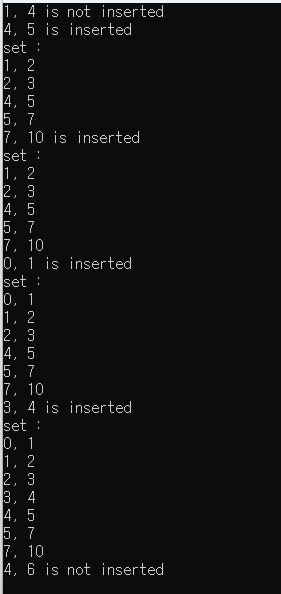
int main()
{
set<pair<int, int>> s;
s.insert({1,2});
s.insert({2,3});
s.insert({5,7});
pair<int, int> arr[6];
arr[0] = {1,4};
arr[1] = {4,5};
arr[2] = {7,10};
arr[3] = {0,1};
arr[4] = {3,4};
arr[5] = {4,6};
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if(insertion(s, arr[i])) {
cout << arr[i].first << ", " << arr[i].second << " is inserted\n";
printSet(s);
}
else
cout << arr[i].first << ", " << arr[i].second << " is not inserted\n";
}
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 최대 유량 문제 (0) | 2025.02.02 |
|---|---|
| 36진법 덧셈, 절대값 뺄셈, 곱셈 (0) | 2024.10.04 |
| C++ map, set struct에 대해 만들기 (0) | 2024.06.22 |
| Index Tree 로 구간 최대값, 최소값, 구간합 구하기 (0) | 2024.06.16 |
| combination, permutation 정리 (0) | 2024.05.01 |

